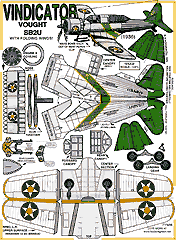
Vindicator - $$4.95
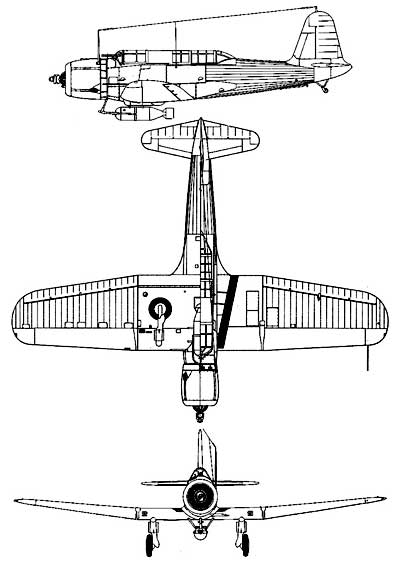
The XSB2U-1 was of conventional low-wing tailwheel monoplane configuration, with the pilot and tail gunner seated in tandem under a long greenhouse-style canopy. Its only remarkable design feature was a propeller with reversible pitch, allowing it to be used to brake the aircraft during a dive bombing attack.
Vought Sikorsky SB2U Vindicator
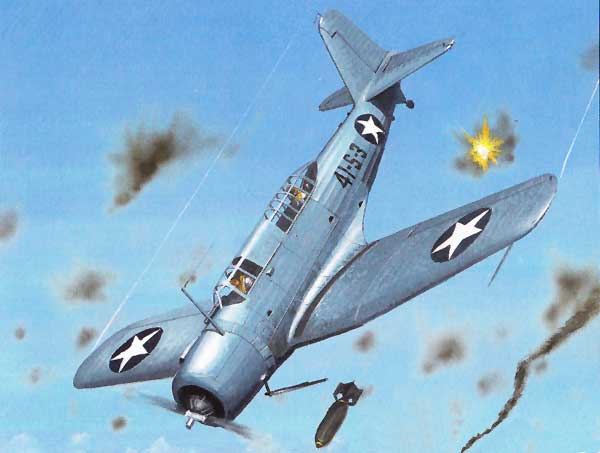


This was the Navy's first monoplane Scout-Bomber opening up a new generation of Navy Aviation in the 30's. By the time the war had started, the Vindicator was sadly outperformed by the Japanese fighters in the Pacific.
This is an important model in your WSAM because of how it bravely ushered in the new era. It's in pre-involvement colors, you'll notice.
An all-metal, low-wing monoplane with two crew seated in tandem beneath a long glasshouse, simple radial engine and retractable undercarriage: the definition was typical of the US Navy scout-bombers and torpedo-bombers of the late thirties-the new generation which followed the classic biplanes and laid the foundation for the combat types of World War II....
Vought Vindicator

An all-metal, low-wing monoplane with two crew seated in tandem beneath a long glasshouse, simple radial engine and retractable undercarriage: the definition was typical of the US Navy scout-bombers and torpedo-bombers of the late thirties-the new generation which followed the classic biplanes and laid the foundation for the combat types of World War II. An aircraft fitting this description in every respect was the XSB2U-1 ordered from Vought on October 11, 1934, as the Navy's first monoplane scout-bomber. Suitability of a monoplane was by no means accepted without question at that time, however, and four months later Vought received a contract for a new biplane scout-bomber prototype, the XSB3U-1, as well.
Both the new Vought prototypes reached Anacostia in April 1936, the XSB2U-1 having first flown on January 4, 1936; comparative trials clearly established the superiority of the monoplane. A production order for 54 SB2U-1s was placed on October 26, 1936, and further work on the biplane was dropped. Completed in July 1937, the SB2U-1was powered by an 825 hp Pratt & Whitney R-1535-96 engine, improving the top speed performance by some 20 mph.
Delivery of the SB2U-1s began on December 20, 1937, to Navy Squadron VB-3. In January 1938 the Navy ordered 58 SB2U-2s with the same engines, differing from the earlier model in having a small increase in gross weight due to new equipment. These were delivered during the latter months of 1938, being followed at the end of 1940 by the first of 57 SB2U-3s ordered on September 25, 1939.
These were the last variants in the series and the first to carry the name Vindicator (aircraft supplied to Britain had previously been named Chesapeake). They had the R-1535-02 engine, increased standard fuel capacity plus provision for long-range tanks for ferry flights, 050-in guns fore and aft, increased armour protection and higher operating weights. One SB2U-l was converted to the XSB2U-3 as a floatplane in 1939, but the production SB2U-3's all served as landplanes.
By 1940, SB2U-1s and SB2U-2s were serving with VB-2 (USS Lexington), VB-3 (Saratoga), VB-4, VS-41 and VS-42 (Ranger) and VS-71 and VS-72 (Wasp). Most of the SB2U-3s were issued to Marine squadrons, primarily equipping VMSB-131 and VMSB-231. These squadrons saw action against Japanese forces in the Pacific during 1942, including the Battle of Midway, but were soon replaced by later types.


 |
Cockpit of the Vought SB2U Vindicator. |
 |
Crew: Two, pilot and gunner |
 |
|||
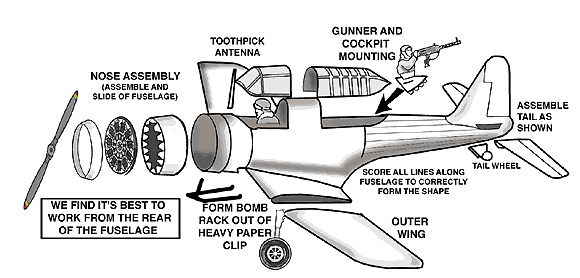
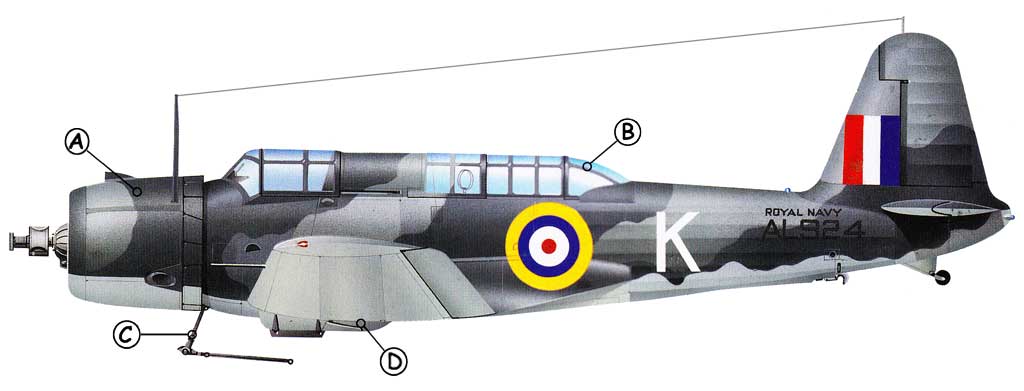
| A: Pratt & Whitney's R-1535 Twin Wasp junior engine powered the SB2U and V-156. This drove a two- bladed metal propeller. | B: The Vindicator had one forward-firing and one free-mounted gun in the rear cockpit, each were .050 cal. machine guns. | C: A 'trapeze' below the cockpit was fitted to a bomb on the centerline pylon, this pulled the bomb downwards and clear of the aircraft. | D: The undercarriage on the Vindicator retracted to the rear and rotated through 9 deg, with the wheels fitting into a recessed bay in each wing. |
 |
One of the seven Vought SB2U-3s destroyed on the field at Ewa. All of VMSB-231's spares (the squadron was embarked in Lexington, en route to Midway, at the time) were thus destroyed. In the background is one of VMSB-232's SBDs. |


