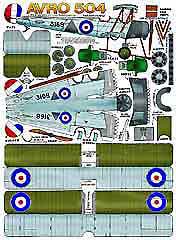
Avro 504 - $$4.50
First flown on 18 September 1913 and powered by an 80 hp Gnome rotary engine, the Avro 504 was a development of the earlier Avro 500, designed for training and private flying. It was a two-bay biplane of all-wooden construction, with a square-section fuselage. Used for many purposes-Trainer, Scout, and even as a WWI Bomber!
WWI Avro 504 British Scout and Trainer


One of the most overlooked and remarkable aircraft of all time is the Avro 503K which first flew at Brooklands July 1913. In a production life spanning well over a decade, some 10,000 504's were built. Some were even still in service at the outbreak of the Second World War!
One of the most famous biplane trainers, the Avro 504 first appeared in 1913 and in the opening stages of World War I operated in bombing and reconnaissance roles with the Royal Flying Corps and the Royal Naval Air Service. However, from 1915 the Awe was assigned the training task for which this aircraft was ideally suited: its docile handling quality endeared it to all who flew it. The main variants were the 504J, 504K, and the postwar 504N. Production exceeded 8600...
Avro 504

|
AVRO 504K (NIGHT-FIGHTER)
The Avro 504 two-seater biplane made the first organized bombing raid in history, on November 21st, 1914. when three R.N.A.S. machines. No's. 873, 874 and 875. attacked the airship sheds at Fried richshafen. The 504 later became an outstandingly successful trainer and was manufactured in large numbers.
 It is less e11
known that three single-seater fighter versions of the 504 were
constructed-one of which equipped operational squadrons as late
as 1918.
It is less e11
known that three single-seater fighter versions of the 504 were
constructed-one of which equipped operational squadrons as late
as 1918.
The Avro 504C was built for the R.N.A.S. for anti Zeppelin and king-distance reconnaissance duties. Based very closely on the two-seater 504B naval trainer, it had an 80 h.p. Gn6me rotary engine enclosed in a swollen-sided cowling. The standard 504 wings had two main spars and ribs of spruce, and were wire-braced and fabric-covered. Long-span ailerons were fitted and there were semi-circular cut-outs in the lower wing-roots. The fuselage had ash longerons and stringers braced by wire, and was fabric covered except for plywood decking round the cockpit, which was cut below the level of the top longerons.
The space occupied by the front cockpit on the 504B was faired over and carried a large petrol tank with a fuel capacity for eight hours' flying. The usual Avro undercarriage with faired-in rubber shock-absorbers and central wooden skid was fitted; the tail-skid was of the pylon variety. The 504C had the me plain rudder and long fin as the 504B~ all the later naval Avro's could be distinguished by their vertical tail surfaces-those of the R.F.C. having the original comma-shaped balanced rudder. The anti-airship 504C carried a Lewis gun fixed to fire upwards through a center-section cutout at an angle of 45 degrees. About eighty 504Cs manufactured.
 A very similar single-seater, the 504D, was built for the R.F.C.
Designed for precisely the same duties, it was, however, based
at the 504A, and had short-span ailerons and a comma-duped rudder.
The engine was the usual 80 h.p. Gn6me rotary. Six of this type
were built.
A very similar single-seater, the 504D, was built for the R.F.C.
Designed for precisely the same duties, it was, however, based
at the 504A, and had short-span ailerons and a comma-duped rudder.
The engine was the usual 80 h.p. Gn6me rotary. Six of this type
were built.
When Major Smith-Barry founded the School of Special Flying at Gosport in August 1917 with the object oft raining flying instructors, he chose the 100 hp. Gn6me Monosoupape Avro 5041 as the best available type for the purpose. Consequently the 5041 was selected as the standard R.F.C. trainer and was built in large numbers. A shortage of the necessary Mono-Gnome engines led to the development at Gosport of the 504K, a model with a universal engine mounting capable of taking any of the available rotaries. The old bulbous enclosed cowling was replaced by a larger open-fronted type. The K supplanted the J as the standard trainer and was eventually used all over the world
Early in 1918 a single-seater version of the K, powered with the 110 h.p. Lc Rhone rotary, was supplied to five Home defense squadrons based on the north side of London. The pilot sat in what was normally the rear cockpit, the front seat being covered in. Some of these K's had a vee-type undercarriage. A Lewis gun was carried on a Foster mounting above the center section. The central gravity tank being moved to port to accommodate it. During the year the type was supplied to other H.D. units outside the London area.
Avro 504A built by modeler Dave Caldwell (one of his first! models) That's a fuel tank on the upper wing. It doesn't get much better than this. |
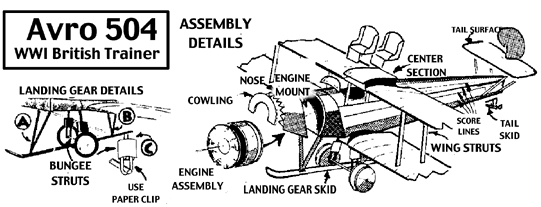
Specifications for the Avro 504K
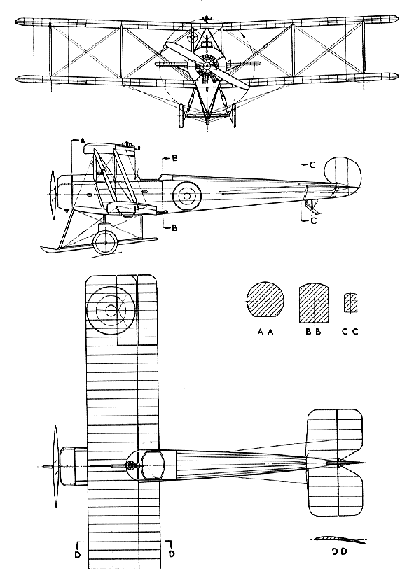 |
Crew: 2 Length: 29 ft 5 in Wingspan: 36 ft Height: 10 ft 5 in Wing area: 330 ft² Empty weight: 1,231 lb Max takeoff weight: 1,829 lb Powerplant: 1× Le Rhône Rotary, 110 hp Performance Maximum speed: 90 mph Cruise speed: 75 mph Range: 250 mi Service ceiling: 16,000 ft Rate of climb: 700 ft/min Wing loading: 5.54 lb/ft² Power/mass: 0.06 hp/lb Climb to 3,500 ft in 5 min |
WWI Avro 504 British Scout and TrainerThe Avro 504 was a versatile British biplane that played a crucial role during World War I as both a scout and trainer aircraft. First flown in 1913, it became the first Allied aeroplane to strafe troops on the ground and conduct a bombing raid over Germany. Widely adopted by the Royal Flying Corps and later the Royal Air Force, it remained the standard trainer until the 1930s, earning the nickname "Trainer of the Empire." Our detailed paper model captures its elegant biplane wings, rotary engine, and historical charm, making it an ideal project for aviation enthusiasts looking to recreate a piece of early 20th-century flight history.
 |
| Very heavy landing in an AVRO 504K. |



