Cessna 152 Private Light Plane
 Extremely
stable tri-gear, side by side two-seater, used mainly as a flying
school trainer. Cessna introduced the swept fin (with extension)
to the small plane market. Speed 123 mph, 480 miles, 100-h.p. Continental
engine.
Extremely
stable tri-gear, side by side two-seater, used mainly as a flying
school trainer. Cessna introduced the swept fin (with extension)
to the small plane market. Speed 123 mph, 480 miles, 100-h.p. Continental
engine.
When Cessna ended production of the Models 120 and 140, it concentrated
upon the development of four-seat aircraft of similar configuration.
It was not until the first flight of the Cessna Model 150, during
September 1957, that the company re-entered the two-seat lightplane
market. An all-metal braced high-wing monoplane, of similar configuration
to the Model 140, this Model 150 differed primarily by the introduction
of non-retractable tricycle landing gear, the installation of dual
controls being optional, and by having a 100-hp Continental 0-200
engine.
Touted as the best aerobatic trainer around. Powered by a 180hp
AEIO-360, this aircraft is stressed to 6 Gs positive and 5 Gs negative.
It is capable of 4 minutes of sustained inverted flight. The symmetrical
wing makes inverted maneuvers a dream.
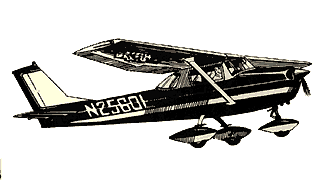
 ZS-NCG Cessna 150 flying merrily by. |
 Cessna 150 flying in Britain |
Cessna 150 looking sweet in the sun |
The Cessna 150/152 is the most used pilot trainer in the world.
Some 56,000 of these popular machines have been manufactured by
Cessna Inc which are in service throughout the world by virtually
all western and some eastern flying training organizations.
The differences between the first three represented varying standards of installed equipment, and there was also a wide range of optional avionics and equipment available. The acrobat embodied structural changes permitting a licence in the Acrobatic category for load factors of +6g and -3g at full gross weight, its aerobatic capability allowing such maneuvers as aileron, barrel and snap rolls, chandelles, loops and vertical reverses.
In 1977, the Cessna 150 range was replaced on the production lines by the basically similar Cessna Model 152. Improvements included a more powerful Avco Lycoming 0-235 engine giving 108-hp, plus installation and cowling changes to reduce engine noise and vibration, together with a McCauley propeller of a modified blade section.
Between 1977 and 1986 the aircraft was available in four versions; the standard Model 152, the slightly heavier Model 152 II with a package of factory installed avionics and omni-directional light beacon, the further improved Model 152 Trainer with other improvements including an intercom system and transponder, and the Model 152 Aerobat with the same aerobatic capabilities as the 150 Aerobat. When production ceased in 1986,7,482 Model l52 and Aerobats had been produced including 640 built under license in France by Reims Aviation.
 At the same time as the deluxe version of the Model 175 appeared
as the Skylark, a similar deluxe version of the Model 172 was
introduced under the name Skyhawk. Further improvements were made
in 1960, with the provision of a new rear fuselage (slimmer and
with rear windows) and a stylish swept vertical tail.
At the same time as the deluxe version of the Model 175 appeared
as the Skylark, a similar deluxe version of the Model 172 was
introduced under the name Skyhawk. Further improvements were made
in 1960, with the provision of a new rear fuselage (slimmer and
with rear windows) and a stylish swept vertical tail.
These modifications were also applied to the Skyhawk and the Skyhawk II, which featured yet more comprehensive equipment, adding sophisticated navigation and communication equipment to blind-flying instrumentation found in the Skyhawk. In March1956 Cessna announced a new Model 182, which was an addition to the standard Skyhawk family, but powered by a 172 -230-hp Continental 0-470-S. It was available in Standard, Skylane and Skylane II versions.
Since that time there has been continuing development and several changes and versions available in 1982 included the Model 172 Skyhawk and Skyhawk II, the Cutlass RG and Cutlass RG II which is basically a re-engineered development of the earlier Model 120 The Model 170 proved popular, but the type's real success started in 1953 when Cessna introduced the Model 17CR: this was powered, like its predecessor, by the 108-kW (145hp( Continental C0145-2 air-tooled piston engine, but incorporated the slotted Fowler flaps pioneered for Cessna's Model 305. With these efficient flaps the field and low-speed performance of the craft.
 |
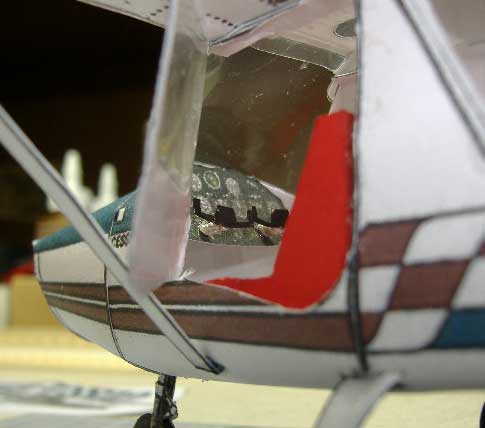
Modeln Pal, Bob Martin, has figured out how to make fabulous clear windscreens and even complex canopies using common clear packing tape. Its easy !! Step by Step instructional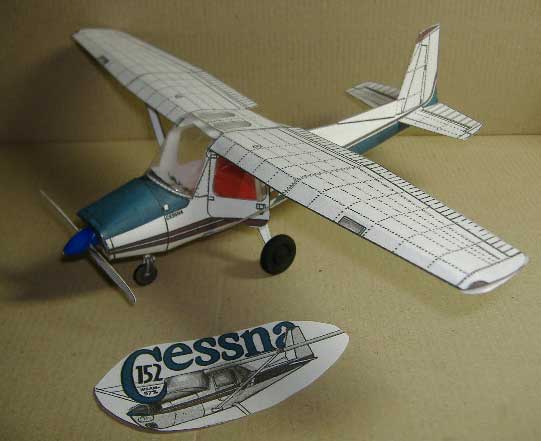 
|
 Construction Tips! Be sure the upper wing surfaces are nicely rolled toward the leading edge before gluing the trailing edge. Taken slowly and smartly, the upper fuselage and wing connection will give you no grief & come out right nicely. |
  |
 |
| Cockpit of the Cessna 152. |
Specifications
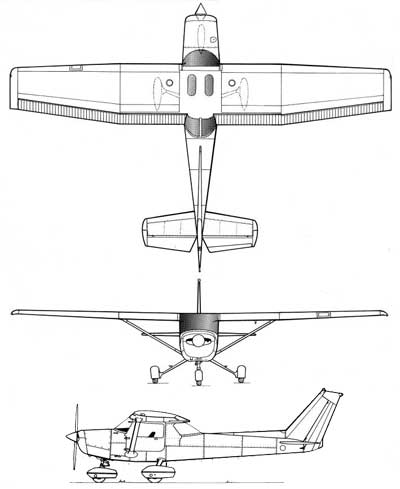 |
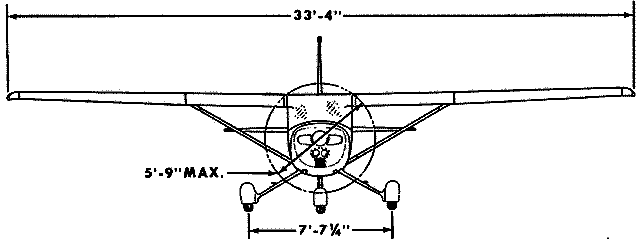
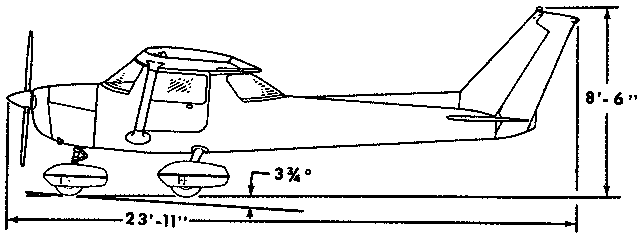
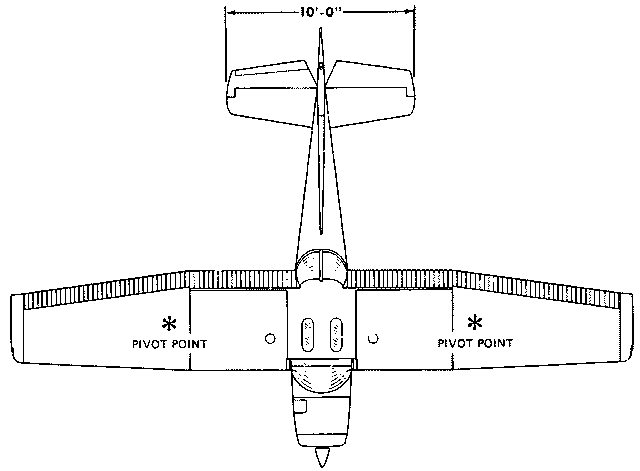
Crew: 1 pilot Capacity: 1 passenger Length: 24 ft 1 in Wingspan: 33 ft 4 in Height: 8 ft 6 in Wing area: 160 ft² Empty weight: 1,081 lb Max takeoff weight: 1,670 lb Powerplant: 1× Lycoming O-235-L2C flat-4 engine, 110 hp driving a 69 in, two-blade, fixed-pitch propeller Performance Maximum speed: 126 mph Cruise speed: 123 mph Stall speed: 49 mph unpowered, flaps down Range: 477 mi Extended range 795 mi with long-range tanks Service ceiling: 14,700 ft Takeoff roll: 725 ft Rate of climb: 715 ft/min Max wing loading: 10.44 lb/ft² Minimum power/mass: .066 hp/lb |

Cessna 150 crashed, sadly, during landing



